
Conversely, Hasselman et al found isolated fibular fracture to cover 57.6% of cases in elderly (> 65 years) women reporting ankle fractures. Werner et al reported an incidence of isolated distal fibula fractures reaching 83% of cases among a population of National Football League athletes reporting ankle fractures.

Distal fibula fractures are more frequent in young active male patients. Age and gender-related differences in ankle fracture epidemiology have been reported. Court-Brown et al reported the following distal fibula fracture type distribution among 1500 ankle fractures: 52% type B trans-syndesmotic fractures, 38% type A infra-syndesmotic fractures and 10% type C supra-syndesmotic fractures. Furthermore, according to the Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Osteosynthesefragen/Orthopaedic Trauma Association (AO/OTA) classification, type B is generally reported to be the more common distal fibula fracture type. Elsoe et al recently reported the epidemiology of 9767 ankle fractures, identifying distal fibula fractures as the most common fracture type, accounting for 55% of cases. Isolated distal fibula fractures represent the most frequent ankle fracture type. Moreover, there has been a sharp increase in osteoporosis related ankle fracture incidence in recent years. The aim of the present paper is to review the most recent literature about the epidemiology, mechanism of injury, diagnosis, classification, management and complications of isolated distal fibula fractures treatment.Īnkle fractures are frequent injuries, accounting for about 9% of all fractures. These include lateral vs posterolateral plating, nonlocking vs locking plate fixation, isolated screws and intramedullary fixation. However, the trend in recent years is headed towards surgical treatment, with advantages in terms of anatomic restoration and earlier recovery.ĭepending on fracture type, displacement and degree of instability, several surgical treatment techniques have been described. Many authors recommend conservative treatment for isolated fibula fractures without signs of ankle instability as good clinical results are obtained in most cases.

These fractures are often the result of a low energy trauma with an external rotation and supination mechanism. In most literature reports, distal fibula fractures represent the majority of ankle fractures. Ankle fractures are frequent injuries, increasing in elderly patients as a consequence of osteoporosis. Fractures of the Ankle Joint: Investigation and Treatment Options. Goost H, Wimmer M, Barg A, Kabir K, Valderrabano V, Burger C. Evaluation of the Syndesmotic-Only Fixation for Weber-C Ankle Fractures with Syndesmotic Injury. CURRENT Diagnosis & Treatment in Orthopedics, Fourth Edition. Musculoskeletal Eponyms: Who Are Those Guys? Radiographics. It was later modified and popularized by the Swiss orthopedic surgeon, Bernhard Georg Weber (1929-2002), in 1972 2. This classification was first described by the Belgian general surgeon, Robert Danis (1880-1962), in 1949. Usually associated with an injury to the medial side Weber C fractures can be further subclassified as 6Ĭ1: diaphyseal fracture of the fibula, simpleĬ2: diaphyseal fracture of the fibula, complexĪ fracture above the syndesmosis results from external rotation or abduction forces that also disrupt the joint Medial malleolus fracture or deltoid ligament injury often presentįracture may arise as proximally as the level of fibular neck and not visualized on ankle films, requiring knee or full-length tibia-fibula radiographs ( Maisonneuve fracture) Tibiofibular syndesmosis disruption with widening of the distal tibiofibular articulation Weber B fractures could be further subclassified as 9ī2: associated with a medial lesion (malleolus or ligament)ī3: associated with a medial lesion and fracture of posterolateral tibiaĪbove the level of the syndesmosis (suprasyndesmotic) Variable stability, dependent on the status of medial structures (malleolus/ deltoid ligament) and syndesmosis may require open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) Tibiofibular syndesmosis usually intact, but widening of the distal tibiofibular joint (especially on stressed views) indicates syndesmotic injuryĭeltoid ligament may be torn, indicated by widening of the space between the medial malleolus and talar dome Usually stable if medial malleolus intact treat with CAM Walker or Moon Boot with crutches and weight bear as tolerated with them for 6 weeksĭistal extent at the level of the syndesmosis (trans-syndesmotic) may extend some distance proximally
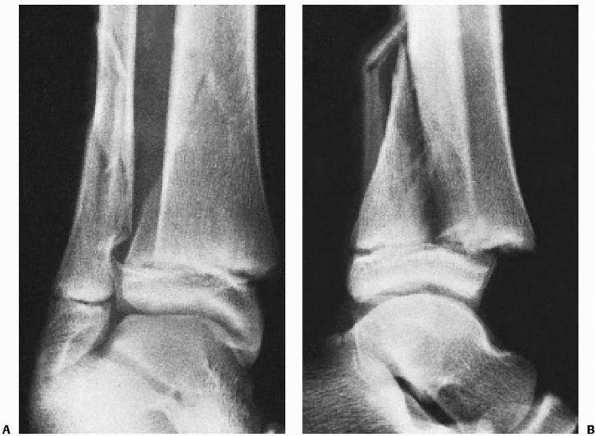
Below the level of the syndesmosis (infrasyndesmotic)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
